
usr/local/maclemon/bin/rsync -recursive -perms -executability -acls -xattrs -owner -group -times -progress "source" "target"This will also preserve ACLs and all extended attributes, forks etc. If you have rsync 3 from mlbackup installed you can use a slight variation which is required for the much superior version of rsync included there. usr/bin/rsync -recursive -perms -executability -owner -group -times -progress -extended-attributes "source" "target" I've included the long options to make the commands easier to comprehend.
Abort dd in unix on mac mac os x#
Puts the contents of foo into /dest with no "foo" directoryįor the Mac OS X bundled rsync 2.6.9 you can use the following line to achieve the same, but with the extra speed of delta copy. In other words, each of the following commands copies the files in the same way, including their setting of the attributes of /dest/foo:Ĭopies "foo" itself to /dest directory creating a foo subdirectoryĬopies "foo/*" to /dest directory implicitely forcing the creation of "foo" at the destination You can think of a trailing / on a source as meaning "copy the contents of this directory" as opposed to "copy the directory by name", but in both cases the attributes of the containing directory are transferred to the containing directory on the destination. P=save intermediate Partial files (-partial) and give you Progress (-progress)Ī trailing slash on the source changes this behavior to avoid creating an additional directory level at the destination. Here's my cheatsheet for rsync, read the man page for it though.
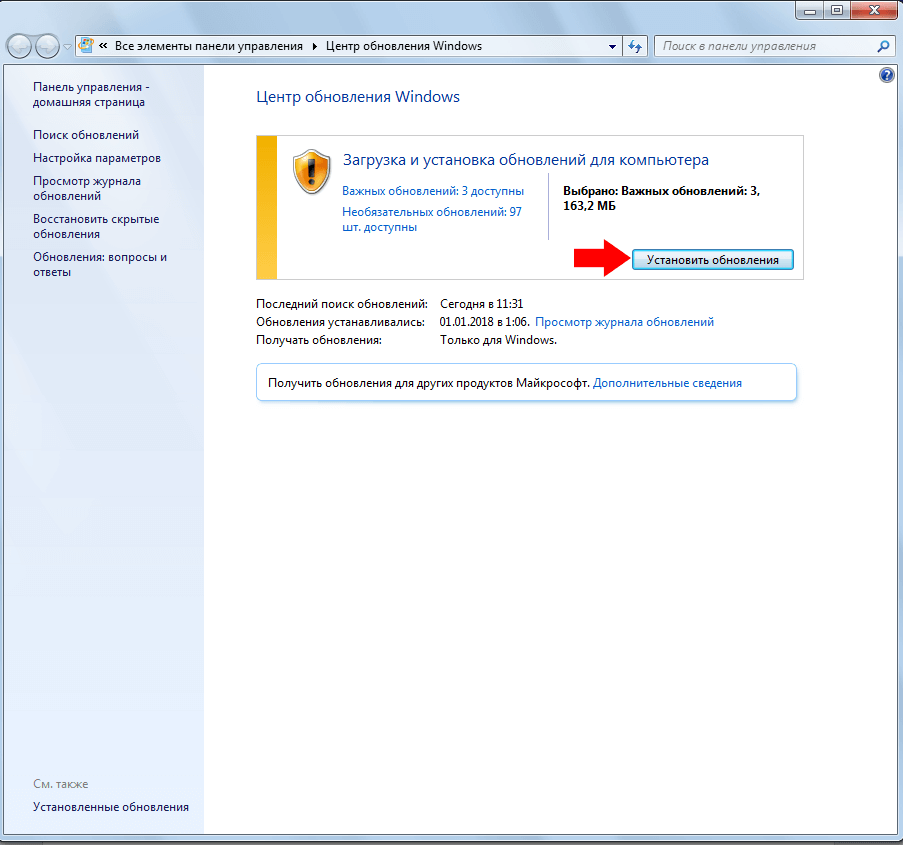
I think cp with these options will overlook changed files, my favorite for stuff like this is rsync. In short, a quick and efficient means of getting just the new photos copied over. The n and R ensure that all new files are copied from the directory tree.
Abort dd in unix on mac software#
So mind-bogglingly simple, and no third-party software required. Whilst rsync could probably do the job, I couldn't get my head around the terminology to be sure I wasn't risking the original files.
Abort dd in unix on mac free#
I checked out numerous commercial and free products for backup, synchronizing and more, and nothing quite fit the bill. My photos are in RAW format (specifically DNG files) and will never change, so I only need to concern myself with new files. My requirements were simple: ensure that all my digital photos, stored on a locally attached USB drive, were duplicated to another drive attached to my AirPort Extreme. While looking for the perfect product to keep my photos safe, I discovered that sometimes simple is best.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
